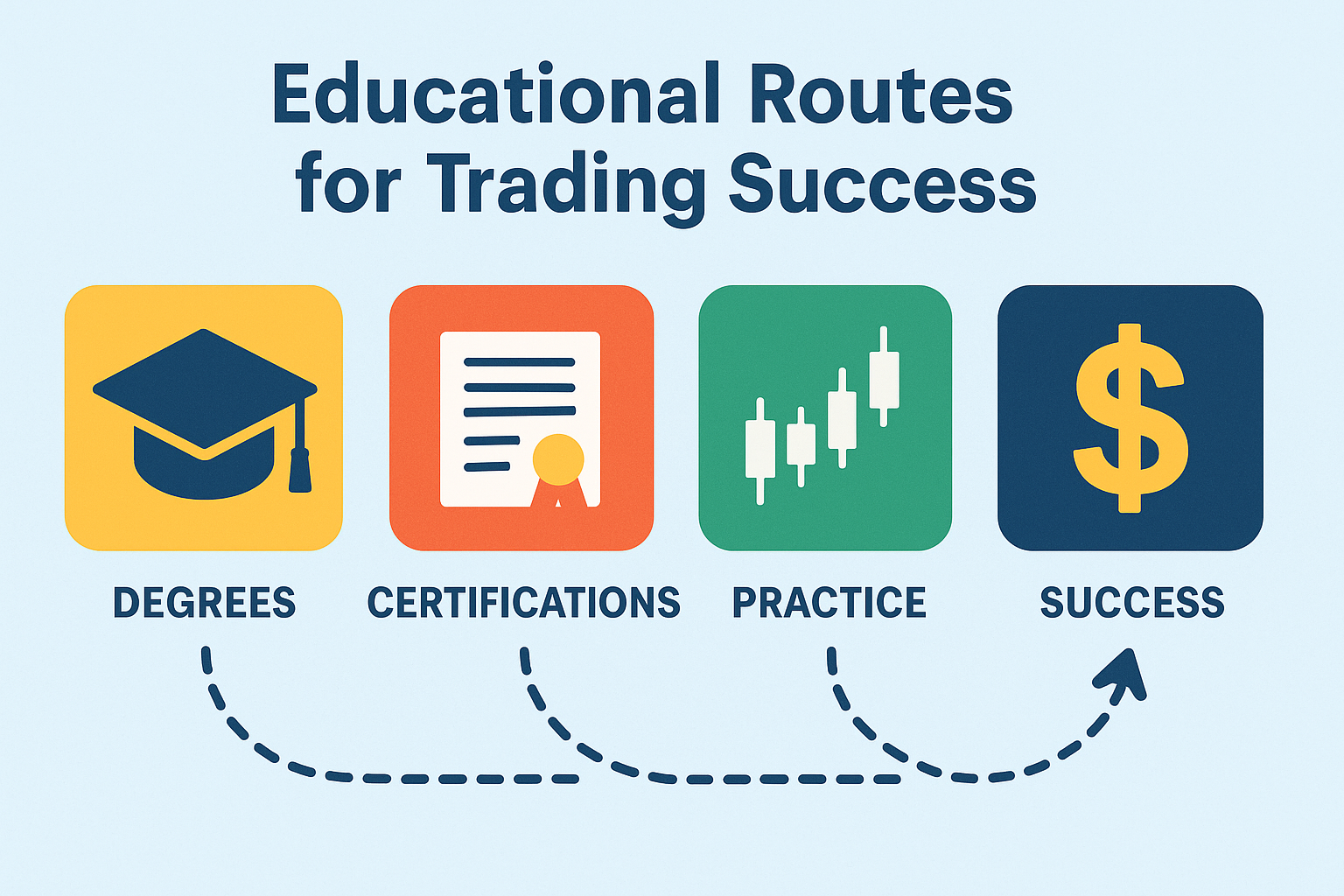
Top 5 Share Market Classes in Chennai (2025 Update)
If you are looking for the top share market classes in Chennai in 2025, the best options include Classroom of Traders, Nifty Trading Academy, BSE Institute Limited, Online Trading Academy, and NSE Academy. These institutes provide structured stock market classes in Chennai that cover beginner to advanced trading, live market practice, and certifications, making them the most trusted choices for anyone serious about learning trading and investing.
Top Share Market Classes in Chennai in 2025
Introduction: Why Stock Market Courses Matter in 2025
Trading in the stock market is no longer limited to financial professionals. In 2025, more individuals in Chennai are exploring trading and investing as career paths and secondary income sources. With India’s financial markets expanding, the demand for stock market classes in Chennai has surged.
The right training institute helps you:
- Understand the fundamentals of equity, derivatives, and forex.
- Learn chart reading, technical analysis, and trading psychology.
- Apply strategies in real markets with confidence.
- Avoid common mistakes beginners make.
This blog reviews the top 5 share market classes in Chennai, comparing their features, course structure, fees, and benefits.
1. Classroom of Traders – Award-Winning Training Institute in Chennai

Why Choose Classroom of Traders?
Classroom of Traders is one of Chennai’s most trusted stock market training institutes. Founded by award-winning trader Mr. Fredrik, the institute focuses on practical, real-world training.

Classroom of Traders is one of the leading stock market training institutes in Chennai, known for transforming beginners into confident traders. The institute is powered by expert mentors like Mr. Fredrick, an award-winning trader and educator, who designs practical strategies tailored for real-world markets. Classroom of Traders offers a structured learning path that covers technical analysis, candlestick patterns, intraday strategies, risk management, and live trading practice. Their speciality lies in blending theory with hands-on exposure, ensuring students not only understand concepts but also apply them successfully in the stock market

Key Features
- Beginner to Advanced Levels: Covers basics to advanced strategies like Elliott Wave, Fibonacci, and price action.
- Hands-On Training: Live trading practice on NSE and global markets.
- Career-Oriented Approach: Suitable for beginners, job seekers, and professionals.
- Free Workshops: Introductory sessions for new learners.
- Updated Syllabus (2025): Incorporates AI-based trading tools and algo-trading basics.
Course Highlights
- Duration: 1–3 months (flexible batch timings).
- Fees: Moderate, with installment options.
- Certification: Industry-recognized completion certificate.
Classroom of Traders Course Syllabus
- Introduction to Stock Market
- Technical Analysis Foundations
- Advanced Technical Strategies
- Derivatives & Options Trading
- Intraday & Swing Trading Strategies
- Risk Management & Psychology
- Live Market Training
- Career & Certification Support
Get a free audit report and strategy plan for this course.
Best For: Students looking for an affordable yet high-quality share market course in Chennai with personalized mentorship.
Social Profiles of classroom of traders :
Contact Details
Address: 18 A, VOC St, Om Sakthi Nagar, Kaikankuppam, Valasaravakkam, Chennai, Tamil Nadu 600087
Phone: 99962234448
Email:info@fredrikedge.com
Website:https://classroomoftraders.com/
2. Nifty Trading Academy (NTA)

Why NTA?
Nifty Trading Academy is a leading stock market coaching center with a strong presence across India.
Key Features
- Nifty & Intraday Focus: Specialized modules on intraday trading and index analysis.
- Practical Learning: Live market case studies.
- Lifetime Mentorship: Continued support after course completion.
Course Highlights
- Covers technical indicators, candlestick patterns, and risk management.
- Online + offline classes available in Chennai.
- Fees: Mid to premium range.
Best For: Traders who want strong training in intraday trading strategies.
Social Profiles :
Contact Details
Phone: 097247 95247
Email:niftytradingacademy@ymail.com
Website:https://www.niftytradingacademy.com/
3. BSE Institute Limited (Chennai Branch)

Why BSE Institute?
Being a subsidiary of the Bombay Stock Exchange, BSE Institute offers world-class financial education.
Key Features
- Industry-Backed Courses: Designed by experts with market experience.
- Certifications: Recognized by employers globally.
- Focus on Investment Banking: Beyond trading, covers corporate finance and compliance.
Course Highlights
- Equity, derivatives, mutual funds, and regulatory framework.
- Blended learning: Classroom + e-learning.
- Premium fees, but high ROI due to brand recognition.
Best For: Students who want a recognized certification for a career in finance and markets.
Social Profiles :
4. Online Trading Academy (OTA) – Chennai

Why OTA?
Online Trading Academy has an international presence with centers in Chennai.
Key Features
- Global Curriculum: Covers Indian and international markets.
- Practical Labs: Simulated trading environments.
- Focus on Lifestyle Trading: Teaches both full-time and part-time trading methods.
Course Highlights
- Modules include equities, forex, futures, and options.
- Online + classroom flexibility.
- Premium fee structure.
Best For: Working professionals seeking global-standard share trading classes in Chennai.
Social Profiles :
5. NSE Academy

Why NSE Academy?
National Stock Exchange (NSE)’s training wing provides professional-grade courses.
Key Features
- SEBI-Recognized Courses: Aligned with regulatory frameworks.
- Industry Trainers: Led by financial experts.
- Certifications: Highly valued in the finance industry.
Course Highlights
- Modules in equity research, derivatives, risk management, and algo-trading.
- Blended online + offline options.
- Fees: Moderate to premium.
Best For: Students aiming for long-term careers in trading and financial services.
Social Profiles :
Why Share Market Classes in Chennai Are Gaining Popularity
Over the past few years, more people have realized that trading is not just for finance professionals. With rising interest in stock trading training in Chennai, both beginners and working professionals are enrolling in structured courses. These programs simplify complex topics like technical analysis, options trading, and risk management into easy-to-learn modules. The availability of share market classes in Chennai in both Tamil and English has also expanded access, making financial education inclusive and practical for the city’s diverse population.
Benefits of Joining the Best Stock Market Course in Chennai
Enrolling in a share market course in Chennai provides more than just textbook knowledge. Students gain hands-on exposure to live market conditions, mentorship from experienced traders, and industry-recognized certifications that open career opportunities. The city’s top trading institutes in Chennai also integrate AI-powered tools and algorithmic trading strategies into their 2025 curriculum, preparing learners for the future of financial markets. Whether your goal is intraday trading, long-term investing, or building a career in finance, the right stock market classes in Chennai can set the foundation for success.
Comparison Table: Top 5 Share Market Classes in Chennai (2025)
| Institute | Focus Area | Duration | Mode | Fees | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classroom of Traders | Practical + Advanced Strategies | 1–3 months | Offline/Online | Moderate | Beginners + Professionals |
| Nifty Trading Academy | Intraday & Nifty Trading | 2–3 months | Both | Mid–Premium | Intraday Traders |
| BSE Institute Limited | Finance + Trading | 3–6 months | Hybrid | Premium | Careers in Finance |
| Online Trading Academy | Global + Multi-Asset Training | 3–6 months | Both | Premium | Professionals, International Focus |
| NSE Academy | SEBI-Recognized Programs | 3–12 months | Hybrid | Mid–Premium | Long-Term Career in Finance & Markets |
Why Chennai is Emerging as a Trading Education Hub
- Growing number of retail traders in Tamil Nadu.
- Chennai’s financial literacy initiatives.
- Proximity to tech hubs driving interest in algo-trading.
- Institutes offering courses in Tamil + English for wider reach.
Conclusion
In 2025, learning stock market trading in Chennai is easier and more structured than ever. Whether you are a beginner or aiming for a career in finance, these top 5 share market classes in Chennai provide the skills, mentorship, and certifications you need.
If you want a practical, affordable, and result-driven share market course in Chennai, Classroom of Traders is a strong choice. For global exposure, institutes like BSE Institute, NSE Academy, and OTA also deliver excellent value.
FAQs – Share Market Classes in Chennai (2025)
1. Which is the best institute for share market classes in Chennai?
The best institute depends on your goals. For practical training, Classroom of Traders is highly recommended. For recognized certifications, BSE Institute and NSE Academy are strong choices.
2. What is the average fee for stock market classes in Chennai?
The average fee ranges from ₹15,000 to ₹80,000, depending on the course level and institute.
3. Can beginners join share market courses in Chennai?
Yes. Most institutes in Chennai have beginner-friendly modules that start with basics like stock market terms, trading accounts, and chart reading.
4. Do share market classes in Chennai include live trading practice?
Yes, leading institutes like Classroom of Traders and Nifty Trading Academy offer live market sessions along with theory.
5. How long does a typical stock market course last in Chennai?
Courses range from 1 month to 12 months. Short-term courses focus on basics, while longer programs cover advanced strategies and certifications.
6. Are stock market courses in Chennai available online?
Yes. Many institutes offer hybrid learning, with both classroom and online training options.
7. What topics are covered in a share market course in Chennai?
Common topics include fundamentals, technical analysis, candlestick charts, derivatives, intraday trading, and risk management.
8. Do these classes cover algo-trading and AI tools in 2025?
Yes. Institutes like NSE Academy and Classroom of Traders have added modules on algo-trading and AI-powered analysis.
9. Can I take a share market course in Chennai in Tamil?
Some institutes provide bilingual training in Tamil and English, making it easier for regional learners.
10. Are there free share trading classes in Chennai?
Yes. Certain institutes offer free workshops or demo sessions before enrolling in paid courses.
11. Do stock market courses in Chennai guarantee jobs?
No course can guarantee a job, but institutes like BSE Institute and NSE Academy provide certifications that improve employability.
12. What is the difference between online and offline share market classes in Chennai?
Offline classes offer face-to-face mentorship, while online classes provide flexibility. Many institutes now use hybrid models for better convenience.
13. Is prior finance knowledge required for share market training?
No. Courses are designed for beginners with no prior finance or trading background.
14. Do these classes cover intraday trading strategies?
Yes. Institutes such as Nifty Trading Academy specialize in intraday and short-term trading techniques.
15. How do I choose the best share market course in Chennai?
Check the course content, trainer experience, practical training options, certification value, fees, and student reviews before enrolling.
16. Are international certifications available from Chennai-based institutes?
Yes. Institutes like BSE Institute and OTA (Online Trading Academy) provide globally recognized certifications.
17. Can working professionals join evening or weekend share market classes in Chennai?
Yes. Flexible batch timings are available, including evening and weekend sessions for professionals.
18. Do these courses provide lifetime mentorship or support?
Some institutes, like Nifty Trading Academy, provide lifetime mentorship and post-course guidance.
19. What career options open after completing a stock market course in Chennai?
You can work as a trader, equity analyst, financial advisor, portfolio manager, or research associate in finance firms.
20. Which share market course in Chennai is best for long-term investors?
Classroom of Traders and NSE Academy offer modules on investment strategies, portfolio building, and wealth management, suitable for long-term investors.