Nifty 50 Today: NSE Market Outlook, Technical Levels & Trading Tips

The best Nifty 50 trading strategy for August 2025 is to combine breakout trading on key resistance levels with strict risk management, while aligning positions to upcoming earnings announcements and global market cues. Traders should focus on intraday setups around the 24,000–24,500 zone, use tight stop-loss levels (below 1% risk per trade), and track institutional activity through OI (Open Interest) shifts. This balanced approach helps capture directional momentum, reduce downside risks, and maximize opportunities in India’s benchmark index during this volatile month.
Nifty 50 as India’s Benchmark Index
The Nifty 50 is India’s most important stock market index. It is managed by the National Stock Exchange of India (NSE) and tracks the performance of the top 50 companies across sectors. Think of it as a scorecard of the Indian economy.
Why Traders and Investors Watch It Closely
- It shows how the overall market is moving.
- Mutual funds, traders, and foreign investors all use it as a benchmark.
- A rise in Nifty usually means confidence in India’s economy.
How Nifty 50 Affects the Overall Stock Market
When Nifty goes up, most stocks also rise, and when it falls, many stocks drop. That’s why traders say, “Follow the Nifty to know the market mood.”
Nifty 50 Performance in August 2025
Market Sentiment and Global Cues
In August 2025, the Indian stock market has been influenced by:
- Hopes of U.S. Fed rate cuts → Cheaper global money flows into India.
- GST reforms talk → Boosts confidence in India’s economy.
- Global growth outlook → Positive signals from Asian and U.S. markets.
Key Drivers
- Fed Chair Jerome Powell’s hint of a rate cut boosted buying in emerging markets.
- S&P’s rating upgrade for India improved investor confidence.
- Foreign Institutional Investors (FIIs) increased their inflows into Indian equities.
Sector-Wise Performance
- IT Sector: Strong, supported by global demand.
- Banking: Stable, but eyes on RBI policy.
- Energy: Mixed, crude oil price volatility is key.
- FMCG: Defensive play, seeing steady demand.
Nifty 50 Technical Outlook for Today
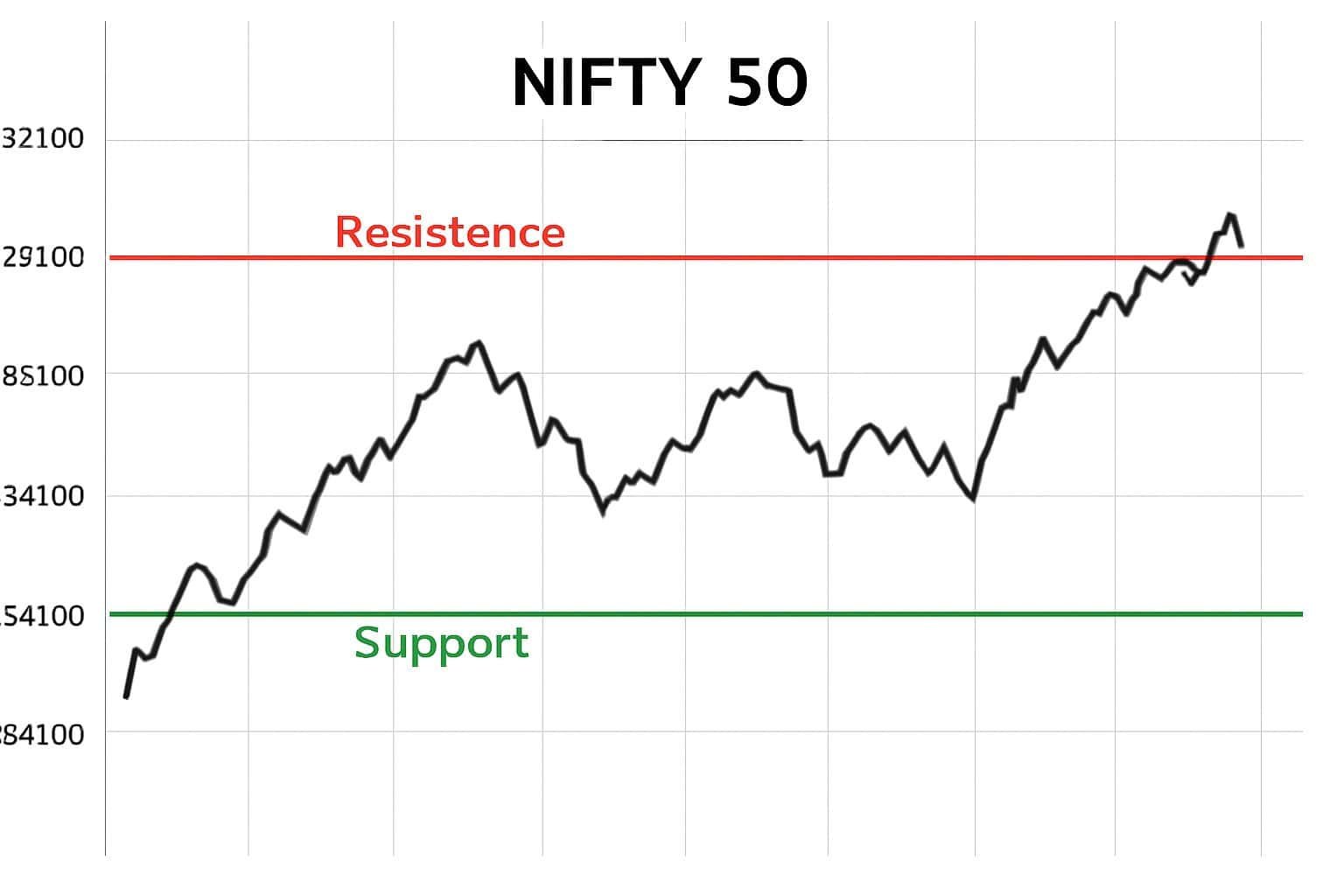
Support and Resistance Levels
- Support: 24,700
- Resistance: 25,150
If Nifty holds above 24,700, it may test 25,150. A breakout above that may push it toward 25,300–25,500.
Intraday Nifty 50 Chart Patterns
Traders are spotting bullish flags and consolidation patterns near resistance.
Moving Averages, RSI, and MACD Analysis
- 50-Day Moving Average (DMA): Uptrend intact.
- RSI (Relative Strength Index): Around 63 – shows moderate strength, not overbought yet.
- MACD: Still bullish, suggesting momentum continues.
What Traders Should Watch This Week
- Nifty’s reaction at 24,700 support.
- If FIIs keep buying.
- RBI statements or policy hints.
Nifty 50 Trading Strategy for August 2025
Advanced Nifty 50 Trading Strategy for August 2025: Options & Hedging Approach
A refined Nifty 50 trading strategy for August 2025 goes beyond simple buy-and-sell. Traders are using options strategies like bull call spreads and iron condors to profit from volatility while limiting risk. For example, buying a 24,800 call and selling a 25,200 call reduces premium cost while still capturing upside moves. Similarly, hedging Nifty futures with protective puts at 24,700 helps manage downside risk. This balanced approach allows traders to participate in rallies without being exposed to sharp market reversals.
Sector Rotation in Nifty 50 Trading Strategy for August 2025
Another powerful Nifty 50 trading strategy for August 2025 is focusing on sector rotation. Data shows IT, energy, and FMCG sectors leading gains, while metals and autos remain weak. Smart traders align their Nifty trades with these sector moves — entering long positions when sector leaders like Infosys or Reliance push the index higher, and trimming exposure when lagging sectors drag performance. By tracking sector rotation alongside index levels, traders gain an edge in timing entries and exits more effectively.
Short-Term Strategy for Intraday Traders
- Buy near support zones (24,700–24,800).
- Book profits near 25,100–25,150.
- Place stop-loss below 24,650.
This keeps risk low while riding market momentum.
Swing Trading Approach (2–10 Days)
- Look for a buy on dips approach.
- Entry: Around 24,700–24,750.
- Exit: 25,300–25,500 range.
Long-Term Investing vs Trading in Nifty 50
Long-term investors don’t chase daily moves. They invest in Nifty 50 index funds or ETFs to track the index over years. Traders, however, use futures & options (F&O) for quick profits.
Risk Management and Position Sizing
- Never risk more than 1%–2% of capital per trade.
- Use stop-losses strictly.
- Adjust position sizes depending on volatility.
Best Sectors and Stocks to Watch in August 2025
Top Performing Nifty 50 Stocks
- Reliance Industries – benefiting from energy reforms.
- Infosys & TCS – IT growth supporting exports.
- HDFC Bank & ICICI Bank – steady performance.
Weak Performers and Possible Risks
- Metal stocks under pressure from global slowdown.
- Auto stocks cautious due to raw material costs.
F&O (Futures and Options) Action
Options data shows heavy call writing at 25,200 → resistance.
Put writing strong at 24,700 → support.
Beginner’s Guide to Trading Nifty 50 Today
How to Start Trading Nifty 50
- Open a Demat and Trading Account with a broker like Zerodha, Upstox, or Groww.
- Add funds via UPI/Netbanking.
- Start with Nifty 50 ETFs or small lots of Nifty Futures.
Simple Example of Buying and Selling Nifty 50
- Buy Nifty at 24,750.
- Sell at 24,900.
- Profit: 150 points per lot (lot size 50 = ₹7,500).
Mistakes Beginners Should Avoid
- Overtrading in excitement.
- Ignoring stop-loss.
- Following random tips without research.
Global Events Affecting Nifty 50 in August 2025
US Fed and Global Interest Rates
A September rate cut could bring more foreign money into India, boosting Nifty further.
Crude Oil, Gold, and Global Commodities Impact
- High crude oil → negative for India (importer).
- Strong gold → safe-haven buying when markets get risky.
Foreign Institutional Investors (FII) Flows
FIIs have been net buyers in August, pushing the Nifty higher.
Nifty 50 Outlook for the Rest of 2025
Bullish and Bearish Scenarios
- Bullish: If Nifty breaks 25,500, it could aim for 26,000+.
- Bearish: A fall below 24,600 could drag it to 24,200.
Expert Forecasts
Analysts suggest a range of 24,500–26,000 till December 2025.
Key Levels to Watch Toward Year-End
- Support: 24,500
- Resistance: 26,000
Final Thoughts – How Traders Can Stay Ahead in Nifty 50
Trading Nifty 50 successfully in August 2025 requires discipline. Watch technical levels, global cues, and sector performance. Beginners should focus on small trades and risk control. Long-term investors can use Nifty 50 ETFs to build steady wealth.
FAQs on Nifty 50 Today and Trading Strategies
Q1. What is the current level of Nifty 50 today?
As of August 25, 2025, Nifty 50 is around 24,939.
Q2. What are the Nifty 50 support and resistance levels this week?
Support at 24,700; resistance at 25,150.
Q3. What is the best trading strategy for Nifty 50 in August 2025?
Buy on dips above 24,700 and target 25,100–25,300, with strict stop-loss.
Q4. Can beginners trade Nifty 50 easily?
Yes, but it’s best to start with ETFs or index funds before moving into Futures & Options.
Q5. Is Nifty 50 a good investment for the long term?
Yes. Historically, Nifty 50 has delivered 12–14% CAGR returns over long periods.
For more insights, strategies, and daily updates on Nifty 50 trading, feel free to reach out to us anytime we’re here to guide you on your trading journey














